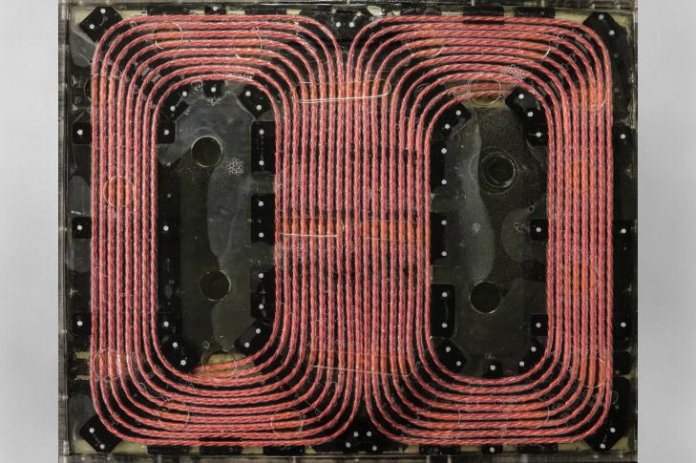
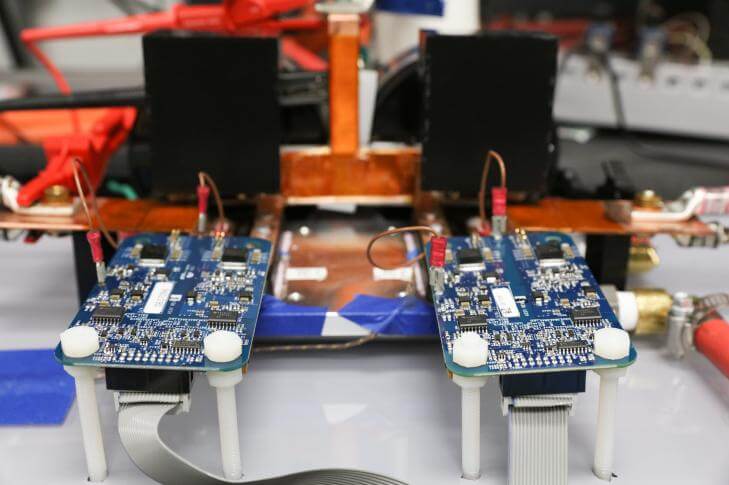
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) have demonstrated a 120 kW wireless charging system for electric vehicles. According to the national lab, this system provides six times the power of previous ORNL technology and represents a big step toward charging times that rival the speed and convenience of a gas station fill-up.
The wireless system transfers 120 kW of power with 97% efficiency, which is comparable to conventional, wired, high-power fast chargers, says ORNL. In the laboratory demonstration, power was transferred across a six-inch air gap between two magnetic coils and charged a battery pack.
ORNL researchers previously created and demonstrated a 20 kW wireless charging system, which is being modified for applications such as commercial delivery trucks.
“It was important to maintain the same or smaller footprint as the previous demonstration to encourage commercial adoption,” says project lead Veda Galigekere of ORNL’s Power Electronics and Electric Machinery Group.
“We used finite element and circuit analyses to develop a novel co-optimization methodology, solving the issues of coil design while ensuring the system doesn’t heat up or pose any safety issues, and that any loss of power during the transfer is minimal,” he explains.
To achieve 120 kW, the ORNL team created a new coil design co-optimized with the latest silicon carbide power electronic devices for a lightweight, compact system.
The system’s architecture takes energy from the grid and converts it to high-frequency alternating current, which generates a magnetic field that transfers power across a large air gap. Once the energy is transferred to the secondary coil, it is converted back to direct current and stored in a vehicle’s batteries, explains the national lab.
The demonstration advances the DOE’s extreme fast-charging goal to develop a system that delivers 350-400 kW and reduces the charging time for electric vehicles to 15 minutes or less.
“This breakthrough significantly advances the technology needed to encourage greater adoption of electric vehicles by increasing their range and the ease of recharging and, in turn, supports an energy-efficient mobility system for the nation’s economic success,” comments Moe Khaleel, associate laboratory director for energy and environmental sciences at ORNL.
ORNL researchers will explore innovations to increase power transfer levels to 200 kW and eventually 350 kW while refining dynamic wireless charging technology. A dynamic system enables the automatic charging of electric vehicles using wireless charging pads installed under roadways. Higher-power charging systems are needed to minimize the cost and complexity of dynamic charging, says ORNL.
“The goal is dynamic charging at highway speeds,” Galigekere says.
The research was funded by the DOE’s Vehicle Technologies Office and performed at the National Transportation Research Center, a DOE user facility at ORNL. ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle LLC for the DOE’s Office of Science.