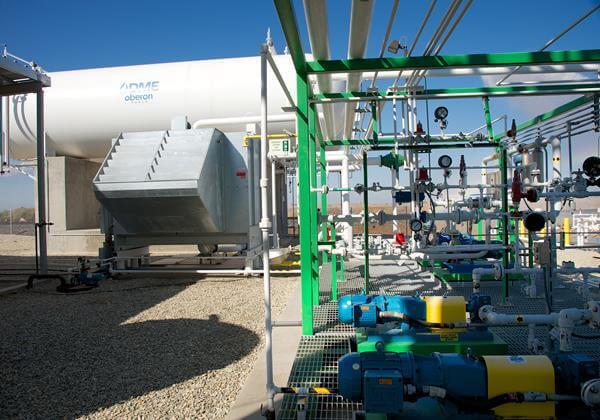
Oberon Fuels, a California-based producer of dimethyl ether (DME), has been awarded a $2.88 million grant from the California Energy Commission (CEC) for a multi-phase project to produce renewable DME as a low-carbon transportation fuel in the U.S.
According to the company, the project unlocks the near- and medium-term decarbonization benefits of rDME. Oberon will upgrade its existing Southern California DME pilot facility to demonstration scale and facilitate the first production of rDME in the U.S.
“With this grant,” says Rebecca Boudreaux, president of Oberon Fuels, “we plan to demonstrate rDME can reduce greenhouse gases and criteria pollutants, replace diesel fuel, maintain performance in existing engines, and provide air quality and economic benefits to rural communities, such as those located within Imperial Valley.”
In addition to scaling up the DME plant and testing new feedstocks, the project will also test modified diesel trucks fueled by rDME in the Imperial Valley and other Southern California locations. Oberon will work with commercial partners to assess the technical feasibility and economics of converting renewable methanol, a byproduct of the pulping process, into rDME and developing associated rDME fueling infrastructure.
“This project will simultaneously address two pressing problems afflicting Imperial Valley by reducing climate change impacts and creating badly needed jobs,” says Assemblymember Eduardo Garcia. “I am thrilled that Oberon Fuels will be demonstrating this new technology in the 56th District, and I look forward to their long-term success and towards making the region a centerpiece for clean fuels.”
According to Oberon, the project is a key building block to the statewide production of rDME from California’s methane. Beyond this project, the technology enhancements will be leveraged into Oberon’s first commercial-scale facility converting dairy biogas to rDME. Oberon will then replicate its initial commercial production facility for statewide rollout of rDME production facilities. These commercial plants will convert in-state methane emissions from dairy manure, food waste and agricultural waste to rDME.
Further, although most of the focus on DME has been on its application as a diesel fuel replacement, it can also serve as a blending agent with propane to reduce carbon intensity when DME is made from renewable feedstocks. With a 20% blend of dairy manure-based rDME, propane’s carbon intensity value can be reduced from 82 to 10, the company estimates.
In addition, because rDME is an efficient hydrogen carrier, rDME can be transported to a hydrogen fueling station and then converted to renewable hydrogen.
“Renewable DME provides an elegant solution to not only the state’s dairy methane challenges but also offers a pathway to zero-emissions for the state’s transportation sector,” notes Elliot Hicks, chief operating officer and co-founder of Oberon Fuels.
Project partners and subcontractors include Alberta-Pacific Forest Industries Inc.; CALSTART; Dynalectric – San Diego; EFR Environmental Services Inc.; ETX LLC, a subsidiary of El Toro Export LLC; Martin Transport; Northern Alberta Institute of Technology; Parafour Innovations; Performance Mechanical Contractors; Prins, a subsidiary of Westport Fuel Systems; Roddey Engineering; and SHV Energy.